About Arsi University
Arsi University
Articles by Arsi University
Comparative analysis of cesarean section using the Robson's Ten-Group Classification System (RTCGS) in private and public hospitals, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia
Published on: 29th June, 2021
OCLC Number/Unique Identifier: 9272361559
Objectives: We analyzed the indications of cesarean section (CS) using Robson Ten-Group.
Classification Systems (RTGCS) and comparison between private and public health facilities in Addis Abeba hospitals, Ethiopia, 2017.
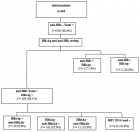
Methods: Facility-based retrospective cross-sectional study was carried out between January 1 and December 31, 2017, including 2411 mothers who delivered by CS were classified using the RTGCS. Data were entered into SPSS version 20 for cleaning and analyzing. Binary logistic regression and AOR with 95% CI were used to assess the determinants of the CS.
Results: The overall CS rate was 41% (34.8% and 66.8% in public & private respectively, p < .0001). The leading contributors for CS rate in the private were Robson groups 5,1,2,3 whereas in the public 5,1,3,2 on descending order. Robson group 1 (nulliparous, cephalic, term, spontaneous labor) and group 3 [Multiparous (excluding previous cesarean section), singleton, cephalic, ≥ 37 weeks’ gestation& spontaneous labor], the CS rate was over two-fold higher in the private than the public sector. Women in Robson groups 1, 2, 5 & 9 are two and more times higher for the absolute contribution of CS in private than public. The top medical indications of CS were non-reassuring fetal status (NRFS, 39.1%) and repeat CS for previous CS scars (39.4%) in public and private respectively. Mothers who delivered by CS in private with history of previous CS scar (AOR 2.9, 95% CI 1.4-6.2), clinical indications of maternal request (AOR 7.7, 95% CI 2.1-27.98) and pregnancy-induced hypertension (AOR 4.2, 95% CI 1.6-10.7), induced labor (AOR 2.5, 95% CI 1.4-4.6) and pre-labored (AOR 2.2, 95% CI 1.6-3.0) were more likely to undergo CS than in public hospital.
Conclusion: The prevalence of CS was found to be high, and was significantly higher in private hospitals than in a public hospital. Having CS scar [having previous CS scar, Robson group 5(Previous CS, singleton, cephalic, ≥ 37 weeks’ gestation) and an indication of repeat CS for previous CS scar] is the likely factor that increased the CS rate in private when compared within the public hospital.
Recommendation: It is important that efforts to reduce the overall CS rate should focus on reducing the primary CS, encouraging vaginal birth after CS (VBAC). Policies should be directed at the private sector where CS indication seems not to be driven by medical reasons solely.
Assessment of early initiation of breastfeeding and determinants among mothers of children under 24 months in Southeast Ethiopia: a community-based cross-sectional study
Published on: 29th October, 2021
OCLC Number/Unique Identifier: 9323491709
Background: Early-initiation of breastfeeding is putting the newborns to the breast within the first hour of life. It is the first critical time they contact their mother outside of the womb. The current study aimed to assess the early initiation of breastfeeding in the study setting. Objectives: To assess the level of early initiation of breastfeeding and its associated factors among mothers who had a baby of less than the age of 24 months in Jeju Woreda, Arsi Zone, Oromia, Ethiopia, 2019.Methods: A community-based cross-sectional study conducted involving 487 mothers from September 18 to October 09, 2019. A multistage sampling technique was employed. First, the setting stratification done in urban and rural settings. Second, ten kebeles selected from both strata. The study participants identified by systematic random sampling technique using kebele log-books registration list as a scheme. The collected data were entered into Epi Info version 7.1.5.0 and exported to SPSS version 21.0.0.0 to analyze. Bivariate and multivariate logistic regression used to determine relations between independent factors and early initiation of breastfeeding. Nine variables became eligible for multivariate analysis at a p - value less than 0.05 in bivariate. The final analyses done the significance of association decided using AOR with its 95% CI, and p - value at less than 0.05. Results: A 97% response rate achieved in this study. The prevalence of early breastfeeding initiation was 74.5%. In multivariate analysis variables namely, mothers whose age category was 35 years and above (AOR = 2.34, 95% CI: (1.07, 5.11)), Pre-lacteal feeding (AOR = 0.37 95% CI (0.17, 0.79)), postpartum advice (AOR = 1.72, 95% CI (1.01, 2.95)) had a significant association. Conclusion and recommendations: The prevalence of early breastfeeding initiation was (74.5%). The finding was low compared to the world health organization recommendation. A working towards discouraging pre-lacteal feeding and strengthening postnatal advice and focusing on ways to better reach young mothers were the recommendations to bring the prevalence in the study area to the recommended level.

HSPI: We're glad you're here. Please click "create a new Query" if you are a new visitor to our website and need further information from us.
If you are already a member of our network and need to keep track of any developments regarding a question you have already submitted, click "take me to my Query."